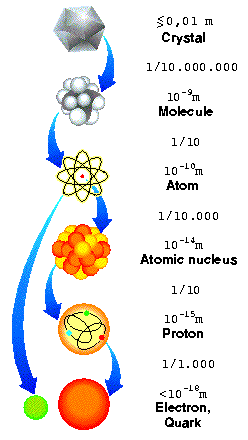

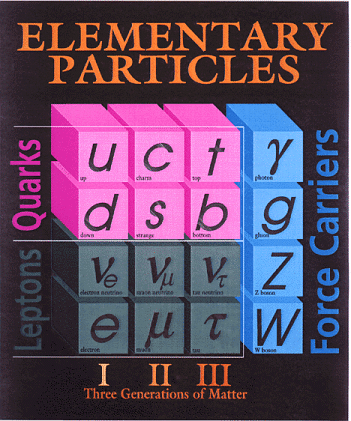
The elementary particles are split into two classes: One class makes up the matter and particles in this class are also called fermions. The second class consists of particles carrying the forces, like the photon which is the carrier of the electromagnetic force. These particles are also called bosons. Apart from the photon there are also the gluons as the carrier of the strong force and the W- and Z-bosons as carrier of the weak force.
The matter particles are further divided into three generations. Particles of the second or third generation behave like the ones in the first generation, except that they are heavier. In the first generation we find two quarks, called the up- and the down-quark, and two leptons: the well-known electron and the neutrino.
The particels can interact with each other. The theory which describes the weak and electromagnetic interaction is called after the inventors Glashow, Salam and Weinberg the GSW-model. The theory of the strong interactions is called quantum chromodynamics. Both theories in common is the underlying gauge principle. The GSW-model is based on a SU(2)xU(1) gauge group, quantum chromodynamics or QCD for short is based on a SU(3) gauge group. Here high energy physics meets mathematics.
How do we know all this ? The answer is simple: from experiments. Experiments in high energy physics usually accelerate two particles before bringing them into collision. A detector around the collision region analysis the outcome of the reaction. The best-known laboratories where these experiments are done are CERN at Geneva, FERMILAB close to Chicago and DESY at Hamburg. Up to now no deviations of the experimental results from the theoretical predictions have been seen.